Halliburton Co. expects the rout in North American shale to peter out after history’s worst crude crash decimated many of its customers.
The world’s biggest provider of fracking signaled that attrition among oilfield service companies is beginning to show results and, in North America at least, a bottom may have been reached, according to a statement on Monday. Overseas is another story, however, because orders there are still weak.
In an illustration of how deeply Halliburton has cut to cope with the crisis, executives revealed Monday that half the company’s North American workforce has been eliminated in the past year. Industrywide, almost one-third of fracking gear has been junked.
The shares rose 3.2% to $12.64 at 10:04 a.m. in New York, after earlier dropping as much as 3.3%.
“The pace of activity declines in the international markets is slowing, while the North America industry structure continues to improve, and activity is stabilizing,” Chief Executive Officer Jeff Miller said in the statement.
The brightening domestic outlook was partly overshadowed by ConocoPhillips’s deal to buy Concho Resources Inc. in a $9.7 billion takeover that will mean one less customer for Halliburton’s services. The combination will result in $500 million in cost cuts, much of those from reduced oil and natural gas exploration.
Oil exploration in North America, which has long been Halliburton’s primary cash cow, has atrophied amid lower crude prices and a global pandemic that sapped energy demand. Customer spending in the U.S. and Canada is contracting for the fourth time in six years and hovering at levels not seen in almost a quarter century, according to Evercore ISI.
Almost two-thirds of Halliburton’s sales came from overseas markets for a second straight quarter, a historic shift for the company.
Excluding severance costs and other charges, Halliburton’s 11-cent per-share profit surpassed the 8-cent average estimate of analysts in a Bloomberg survey. Sales of $3 billion were just shy of the $3.1 billion average forecast.
Changing Course
The 101-year-old oilfield-service provider is in the midst of what it calls a “fundamentally different course” that involves cutting more than $1 billion in costs and looking outside of North America for better growth. Miller has also dismissed thousands of workers and clipped Halliburton’s dividend.
But growth in oilfield work anywhere in the world will be hard to come for an extended period. Larger rival Schlumberger warned investors late last week not to expect growth over the final three months of the year and said it’ll be 2022 before overseas drilling picks up.
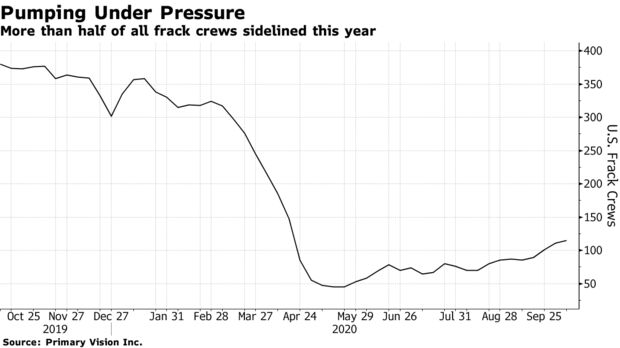
Hydraulic fracturing, which blasts water, sand and chemicals underground to release trapped hydrocarbons, could see a slight uptick thanks to the mountain of pre-drilled wells waiting to be completed, Schlumberger executives said. After plummeting to a record low in May, the number of frack crews working in U.S. fields has climbed back above 100, but is still down by more than half since the start of the year, according to Primary Vision Inc.

No comments:
Post a Comment